How To Spot Bunions
Overview
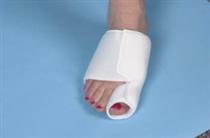 A bunion looks like a bump on the inside of the foot where the big toe joins the foot. Over time, the bunion gets worse. The big toe starts to lean toward neighboring toes instead of pointing straight ahead. (The scientific name for this is hallux valgus or hallux abducto valgus.) The bump is a sign that the bones of the foot are out of alignment. While shoes with high heels or pointed toes may cause the joint to ache, they don't cause bunions. Most often they are due to an inherited foot structure. The tendons and ligaments that hold bones and muscles together at the joint are not working as they should. This structure makes it more likely that a person will develop a bunion.
A bunion looks like a bump on the inside of the foot where the big toe joins the foot. Over time, the bunion gets worse. The big toe starts to lean toward neighboring toes instead of pointing straight ahead. (The scientific name for this is hallux valgus or hallux abducto valgus.) The bump is a sign that the bones of the foot are out of alignment. While shoes with high heels or pointed toes may cause the joint to ache, they don't cause bunions. Most often they are due to an inherited foot structure. The tendons and ligaments that hold bones and muscles together at the joint are not working as they should. This structure makes it more likely that a person will develop a bunion.
Causes
Bunions are a common problem that can cause foot pain and difficulty wearing shoes. Bunions occur in about 30% of the population of most Western countries. They are seen most commonly in women and become more common as people get older. Patients with bunions generally have one of two problems that can cause pain. As the big toe becomes more and more angled (pointing toward the other toes), the base of the toe becomes more and more prominent, forming the bunion. The bunion forms in part because of the new angle of the toe, and in part due to inflammation over the bunion surface. As the inflammation worsens, people can experience pain with shoe wear and walking. The big toe may eventually come to lie over, or more commonly under, the second toe. This may cause further irritation while wearing shoes and more pain. The second toe of patients who have bunions commonly forms a hammer toe.
Symptoms
Most patients complain of pain directly on the bunion area, within the big toe joint, and/or on the bottom of the foot. The bunion may become irritated, red, warm, swollen and/or callused. The pain may be dull and mild or severe and sharp. The size of the bunion doesn?t necessarily result in more pain. Pain is often made worse by shoes, especially shoes that crowd the toes. While some bunions may result in significant pain, other bunions may not be painful at all.
Diagnosis
Most patients are diagnosed to have bunions from clinical history and examination. However, in some cases, X-rays will be performed to determine the extent of damage to the joint. Furthermore, it will enable the treating doctor to decide on the best course of management of the patient.
Non Surgical Treatment
Wearing good footwear does not cure the deformity but may ease symptoms of pain and discomfort. Ideally, get footwear advice from a person qualified to diagnose and treat foot disorders (podiatrist - previously called a chiropodist). Advice may include wear shoes, trainers or slippers that fit well and are roomy. Don't wear high-heeled, pointed or tight shoes. You might find that shoes with laces or straps are best, as they can be adjusted to the width of your foot. Padding over the bunion may help, as may ice packs. Devices which help to straighten the toe (orthoses) are still occasionally recommended, although trials investigating their use have not found them much better than no treatment at all. Painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen may ease any pain. If the bunion (hallux valgus) develops as part of an arthritis then other medication may be advised. A course of antibiotics may be needed if the skin and tissues over the deformity become infected. 
Surgical Treatment
As you explore bunion surgery, be aware that so-called "simple" or "minimal" surgical procedures are often inadequate "quick fixes" that can do more harm than good. And beware of unrealistic claims that surgery can give you a "perfect" foot. The goal of surgery is to relieve as much pain, and correct as much deformity as is realistically possible. It is not meant to be cosmetic. There are several techniques available, often as daycare (no in-patient stay), using ankle block local anaesthetic alone or combined with sedation or full general anaesthesia. Most of the recovery occurs over 6-8 weeks, but full recovery is often longer and can include persistent swelling and stiffness. The surgeon may take one or more of the following steps in order to bring the big toe back to the correct position: (a) shift the soft tissue (ligaments and tendons) around the joint and reset the metatarsal bone (osteotomy), remove the bony bump and other excess bone or (b) remove the joint and connect (fuse) the bones on the two side of the joint (fusion). These are just a few examples of the many different procedures available and your treating surgeon can help you decide the best option for you.
Is Overpronation Of The Foot
Overpronation is the most common abnormality found in the foot, and for this reason, is the most studied. The term that most people attribute to overpronation is ?flat feet.? Pronation is the rolling in of the foot and the collapse of the arch. Every person pronates to some extent and this is a necessary moment in the normal walking cycle as it allows the forefoot to make complete contact with the ground. A foot that overpronates acts like a loose bag of bones during the walking cycle. This makes this type of foot very flexible but inefficient. The foot has to work much harder to propel the body, fatiguing easily and placing mechanical stresses on the lower body. We like to use the analogy of digging a hole in the dirt. Overpronating feet are like using a broom to dig the hole. It won?t break down quickly, but you will be digging for a very long time, or until eventually wear and tear will take effect. Wouldn?t you rather have a shovel to work with. This is in essence what an orthotic can do for your feet. This is why orthotics have become an evidence based treatment for so many foot ailments, as they can effectively manage overpronation.Overpronation is when a person pronates too much and for too long. This places excess stress on the tendons and ligaments in the foot and ankle.

Causes
You do not have to be a runner or athlete to suffer from overpronation. Flat feet can be inherited, and many people suffer from pain on a day-to-day basis. Flat feet can also be traumatic in nature and result from tendon damage over time. Wearing shoes that do not offer enough arch support can also contribute to overpronation.
Symptoms
Overpronation can lead to injuries and pain in the foot, ankle, knee, or hip. Overpronation puts extra stress on all the bones in the feet. The repeated stress on the knees, shins, thighs, and pelvis puts additional stress on the muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the lower leg. This can put the knee, hip, and back out of alignment, and it can become very painful.
Diagnosis
Do the wet foot test. Get your feet wet and walk along a paved surface or sand and look at the footprints you leave. If you have neutral feet you will see a print of the heel with a thin strip connecting to your forefoot, but if you're overpronating your foot print will look a bit like a giant blob with toes.
Non Surgical Treatment
There are exercises that you can do to help deal with the effects and treat the cause. Obviously you can opt for an insert into your shoe either by way of your sports shop or go see a podiatrist. Like anything in your body that is not working correctly; you will have to manage your condition. Don't put off dealing with the problem as it will manifest associated issues along the alignment and as far up as your neck. If it's mild pronantion, I suggest running barefoot. If you can't do this then don't wear shoes at all at home or in the office as much as possible. Give your calf muscles a huge stretch everyday as these with the ligaments from the foot up to the muscle get tight and are linked to your pain. Loosen your calf muscles as much as possible. Great exercise is to sit barefoot with a marble on the floor in front of you. Grab the marble with your toes and try to hold it tight in the middle of the base of your foot. Ping pong balls and even golf balls work. Do this each night and combined with calf stretches you'll start to correct the muscle alignment gradually in the foot. Put more attention into massaging your feet, standing with a good posture, stretching your feet, ankles and calf muscles. Lastly, if you are fat this will not help at all. You must lose weight swimming, cycling and eradicating sugar and fat from your diet. The added strain on the foot by being a fat body compounds the problems and inhibits corrective results that you are after.
Prevention
Custom-made orthotics will reduce the twisting of the leg muscles as they enter the foot, by maintaining a normal alignment of the bones and joints of the foot. If the bones and joints are aligned properly, by reducing the pronation, the muscles can run straight to their attachments in the foot, without twisting to get to these bones. This action of custom-made orthotics will reduce Achilles Tendonitis shin splints; ankle, knee, hip, and lower back pain; and leg cramps. This action will also allow the leg muscles to work more efficiently, thus allowing you to walk and run with less effort.
Dealing With Calcaneal Apophysitis
This condition is self limiting, it will go away when the two parts of bony growth join together, this is natural. Unfortunately, Sever's disease can be very painful and limit sport activity of the child while waiting for it to go away, so treatment is often advised to help relieve it. In a few cases of Sever's disease, the treatment is not successful and these children will be restricted in their activity levels until the two growth areas join, usually around the age of 16 years. There are no known long term complications associated with Sever's disease.
Causes
This condition is more common in boys than girls. It generally presents between the ages of 9-14 and peaks between ages 10-12 years. This injury can reoccur up until the age of 17, when the growth plate of the calcaneous generally closes. These types of injuries will commonly occur during periods of rapid growth. Sever?s Disease occurs more frequently in child with flat feet, but all children with flat feet will not get Sever?s.
Symptoms
Sever condition causes pain at the back of the heel. The pain is increased with plantar flexion of the ankle (pushing down with the foot as if stepping on the gas), particularly against resistance. Sever condition also causes tenderness and swelling in the area of the pain.
Diagnosis
You may have pain when your doctor squeezes your heel bone. You may have pain when asked to stand or walk on your toes or on your heels. You may have pain in your heel when your doctor stretches your calf muscles. Your doctor may order x-rays of the injured foot to show an active growth plate.
Non Surgical Treatment
The primary method of treating Sever?s disease is taking time off from sports and other physical activities to alleviate the pressure on the heel bone. During the healing period, your child?s doctor may also recommend physical therapy or any type of exercise that involves stretching and strengthen leg muscles and tendons. Wrapping ice in a towel and placing it under the child?s heel will also help to alleviate and reduce pain and swelling.
Recovery
If the child has a pronated foot, a flat or high arch, or another condition that increases the risk of Sever's disease, the doctor might recommend special shoe inserts, called orthotic devices, such as heel pads that cushion the heel as it strikes the ground, heel lifts that reduce strain on the Achilles tendon by raising the heel, arch supports that hold the heel in an ideal position, If a child is overweight or obese, the doctor will probably also recommend weight loss to decrease pressure on the heel. The risk of recurrence goes away on its own when foot growth is complete and the growth plate has fused to the rest of the heel bone, usually around age 15.
What Is Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction ?
Overview
When we have foot pain, it isn?t always easy to pinpoint the source because we can?t visualize the structure of all the bones, muscles, and tendons on the inside. The posterior tibial tendon plays an important supportive role within the structure of the foot. It attaches to your calf muscle and then comes down along the inside of your ankle, connecting to the bones inside your foot at the other side. This tendon?s main function is to hold up your arch and support your foot during each and every movement. Every step, run, walk, or jump is made possible with the support from this crucial tendon. While it is designed to perform such an important role, it is vulnerable to stress and injury. A tear during a traumatic injury or stress from overuse can injure the tissues within the tendon. This kind of injury is referred to as posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD). A really hard fall during a sports game or exposure to a repetitive motion, such as the impact on feet during soccer, tennis, football or basketball, can cause an injury. Flat foot and flat feet in adults can exacerbate this condition. The tendon can experience small tears and become inflamed. If the inflammation is allowed to continue and worsen over time, it will weaken further and could rupture completely. 
Causes
Obesity - Overtime if your body is carrying those extra pounds, you can potentially injure your feet. The extra weight puts pressure on the ligaments that support your feet. Also being over weight can lead to type two diabetes which also can attribute to AAFD. Diabetes - Diabetes can also play a role in Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity. Diabetes can cause damage to ligaments, which support your feet and other bones in your body. In addition to damaged ligaments, uncontrolled diabetes can lead to ulcers on your feet. When the arches fall in the feet, the front of the foot is wider, and outer aspects of the foot can start to rub in your shoe wear. Patients with uncontrolled diabetes may not notice or have symptoms of pain due to nerve damage. Diabetic patient don?t see they have a problem, and other complications occur in the feet such as ulcers and wounds. Hypertension - High blood pressure cause arteries narrow overtime, which could decrease blood flow to ligaments. The blood flow to the ligaments is what keeps the foot arches healthy, and supportive. Arthritis - Arthritis can form in an old injury overtime this can lead to flatfeet as well. Arthritis is painful as well which contributes to the increased pain of AAFD. Injury - Injuries are a common reason as well for AAFD. Stress from impact sports. Ligament damage from injury can cause the bones of the foot to fallout of ailment. Overtime the ligaments will tear and result in complete flattening of feet.
Symptoms
Symptoms are minor and may go unnoticed, Pain dominates, rather than deformity. Minor swelling may be visible along the course of the tendon. Pain and swelling along the course of the tendon. Visible decrease in arch height. Aduction of the forefoot on rearfoot. Subluxed tali and navicular joints. Deformation at this point is still flexible. Considerable deformity and weakness. Significant pain. Arthritic changes in the tarsal joints. Deformation at this point is rigid.
Diagnosis
Although you can do the "wet test" at home, a thorough examination by a doctor will be needed to identify why the flatfoot developed. Possible causes include a congenital abnormality, a bone fracture or dislocation, a torn or stretched tendon, arthritis or neurologic weakness. For example, an inability to rise up on your toes while standing on the affected foot may indicate damage to the posterior tibial tendon (PTT), which supports the heel and forms the arch. If "too many toes" show on the outside of your foot when the doctor views you from the rear, your shinbone (tibia) may be sliding off the anklebone (talus), another indicator of damage to the PTT. Be sure to wear your regular shoes to the examination. An irregular wear pattern on the bottom of the shoe is another indicator of acquired adult flatfoot. Your physician may request X-rays to see how the bones of your feet are aligned. Muscle and tendon strength are tested by asking you to move the foot while the doctor holds it.
Non surgical Treatment
Nonoperative treatment of stage 1 and 2 acquired adult flatfoot deformity can be successful. General components of the treatment include the use of comfort shoes. Activity modification to avoid exacerbating activities. Weight loss if indicated. Specific components of treatment that over time can lead to marked improvement in symptoms include a high repetition, low resistance strengthening program. Appropriate bracing or a medial longitudinal arch support. If the posterior tibial tendon is intact, a series of exercises aimed at strengthening the elongated and dysfunctional tendon complex can be successful. In stage 2 deformities, this is combined with an ankle brace for a period of 2-3 months until the symptoms resolve. At this point, the patient is transitioned to an orthotic insert which may help to support the arch. In patients with stage 1 deformity it may be possible to use an arch support immediately. 
Surgical Treatment
Stage two deformities are less responsive to conservative therapies that can be effective in mild deformities. Bone procedures are necessary at this stage in order to recreate the arch and stabilize the foot. These procedures include isolated fusion procedures, bone grafts, and/or the repositioning of bones through cuts called osteotomies. The realigned bones are generally held in place with screws, pins, plates, or staples while the bone heals. A tendon transfer may or may not be utilized depending on the condition of the posterior tibial tendon. Stage three deformities are better treated with surgical correction, in healthy patients. Patients that are unable to tolerate surgery or the prolonged healing period are better served with either arch supports known as orthotics or bracing such as the Richie Brace. Surgical correction at this stage usually requires fusion procedures such as a triple or double arthrodesis. This involves fusing the two or three major bones in the back of the foot together with screws or pins. The most common joints fused together are the subtalar joint, talonavicular joint, and the calcaneocuboid joint. By fusing the bones together the surgeon is able to correct structural deformity and alleviate arthritic pain. Tendon transfer procedures are usually not beneficial at this stage. Stage four deformities are treated similarly but with the addition of fusing the ankle joint.
Understand Heel Ache

When walking, your heels repeatedly hit the ground with considerable force. They have to be able to absorb the impact and provide a firm support for the weight of the body. When pain develops in the heel, it can be very disabling, making every step a problem, affecting your posture. There are various types of heel Heel Pain. Some of the most common are heel spurs (plantar fasciitis); heel bursitis and heel bumps.
Causes
Heel pain has a number of causes that are typically associated with overuse of the heel bone. You can strain your heel by pounding your feet on hard surfaces, being overweight, or wearing shoes that do not fit properly. These strains can irritate the heel?s bones, muscles, or tendons. Other common causes of heel pain include the following. Heel Spurs. Heel spurs develop when the lining that covers the heel is continuously stretched. When this occurs, pieces of the lining may break off. Heel spurs typically develop in athletes who frequently run or jog. They are also common in people who are obese. Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar fasciitis develops when the tissue connecting the heel to the ball of the foot becomes inflamed. Plantar fasciitis also occurs in athletes who frequently run or jog. It can also result from wearing shoes that do not fit properly. Excessive Pronation. Excessive pronation occurs when the ligaments and tendons at the back of the heel are stretched too much. This condition can occur when injuries to the back, hips, or knees change the way you walk. Achilles Tendinitis. Achilles tendinitis can occur when the Achilles tendon, which runs along the back of the heel, becomes inflamed. This condition is common in people with active lifestyles who frequently run and jog, professional athletes and dancers.
Symptoms
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis are pain on the bottom of the heel, pain in the arch of the foot, pain that is usually worse upon arising, pain that increases over a period of months. People with plantar fasciitis often describe the pain as worse when they get up in the morning or after they?ve been sitting for long periods of time. After a few minutes of walking the pain decreases, because walking stretches the fascia. For some people the pain subsides but returns after spending long periods of time on their feet.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is generally made during the history and physical examination. There are several conditions that can cause heel pain, and plantar fasciitis must be distinguished from these conditions. Pain can be referred to the heel and foot from other areas of the body such as the low back, hip, knee, and/or ankle. Special tests to challenge these areas are performed to help confirm the problem is truly coming from the plantar fascia. An X-ray may be ordered to rule out a stress fracture of the heel bone and to see if a bone spur is present that is large enough to cause problems. Other helpful imaging studies include bone scans, MRI, and ultrasound. Ultrasonographic exam may be favored as it is quick, less expensive, and does not expose you to radiation. Laboratory investigation may be necessary in some cases to rule out a systemic illness causing the heel pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Reiter's syndrome, or ankylosing spondylitis. These are diseases that affect the entire body but may show up at first as pain in the heel.
Non Surgical Treatment
If pain and other symptoms of inflammation?redness, swelling, heat?persist, you should limit normal daily activities and contact a doctor of podiatric medicine. The podiatric physician will examine the area and may perform diagnostic X-rays to rule out problems of the bone. Early treatment might involve oral or injectable anti-inflammatory medication, exercise and shoe recommendations, taping or strapping, or use of shoe inserts or orthotic devices. Taping or strapping supports the foot, placing stressed muscles and tendons in a physiologically restful state. Physical therapy may be used in conjunction with such treatments. A functional orthotic device may be prescribed for correcting biomechanical imbalance, controlling excessive pronation, and supporting of the ligaments and tendons attaching to the heel bone. It will effectively treat the majority of heel and arch pain without the need for surgery. Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require more advanced treatments or surgery. If surgery is necessary, it may involve the release of the plantar fascia, removal of a spur, removal of a bursa, or removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
Surgical Treatment
It is rare to need an operation for heel pain. It would only be offered if all simpler treatments have failed and, in particular, you are a reasonable weight for your height and the stresses on your heel cannot be improved by modifying your activities or footwear. The aim of an operation is to release part of the plantar fascia from the heel bone and reduce the tension in it. Many surgeons would also explore and free the small nerves on the inner side of your heel as these are sometimes trapped by bands of tight tissue. This sort of surgery can be done through a cut about 3cm long on the inner side of your heel. Recently there has been a lot of interest in doing the operation by keyhole surgery, but this has not yet been proven to be effective and safe. Most people who have an operation are better afterwards, but it can take months to get the benefit of the operation and the wound can take a while to heal fully. Tingling or numbness on the side of the heel may occur after operation.
Prevention

Heel pain is commonly caused from shoes that do not fit properly. In addition, shoes need to have ample cushioning and support, particularly through the heel, ball of the foot, and arch. Shoes should also be replaced if they become too worn. One sure sign of wear and tear is overly worn areas of a shoe's insoles. If the heel or ball of the foot is particularly worn, damage could easily occur since the bottom of the foot is not getting the cushioning it needs.
What's The Major Cause Of Achilles Tendinitis ?
 If you have pain along the back of your leg near your heel, you may have Achilles tendonitis. Achilles tendonitis is an overuse injury that commonly occurs in runners and ?weekend warriors?. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. Named after a tragic hero from Greek mythology, it connects your calf muscle to your heel bone to allow you to jump, run and walk. Achilles tendonitis is most common in middle-aged men, but it can happen to anyone who has a sudden increase in physical activity. The risk is increased if you also have tight calf muscles and/or a flat arch in your foot. Other risk factors include running in worn out shoes, cold weather, frequently running uphill or if you suffer from medical conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure. There are two main types of Achilles tendinitis: insertional and noninsertional. Insertional Achilles tendinitis involves the lower portion of the heel, where the tendon attaches to the heel bone. Noninsertional Achilles tendinitis is when the fibers in the middle portion of the tendon have started to break down with tiny tears, swell, and/or thicken. This type is more often seen in younger, active people. Both types can also cause bone spurs. Achilles tendonitis should be diagnosed by your doctor. However, if you experienced a sudden ?pop? in the back of your calf or heel, this might be something more serious like a ruptured or torn Achilles tendon. If this happens, see your doctor immediately.
If you have pain along the back of your leg near your heel, you may have Achilles tendonitis. Achilles tendonitis is an overuse injury that commonly occurs in runners and ?weekend warriors?. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. Named after a tragic hero from Greek mythology, it connects your calf muscle to your heel bone to allow you to jump, run and walk. Achilles tendonitis is most common in middle-aged men, but it can happen to anyone who has a sudden increase in physical activity. The risk is increased if you also have tight calf muscles and/or a flat arch in your foot. Other risk factors include running in worn out shoes, cold weather, frequently running uphill or if you suffer from medical conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure. There are two main types of Achilles tendinitis: insertional and noninsertional. Insertional Achilles tendinitis involves the lower portion of the heel, where the tendon attaches to the heel bone. Noninsertional Achilles tendinitis is when the fibers in the middle portion of the tendon have started to break down with tiny tears, swell, and/or thicken. This type is more often seen in younger, active people. Both types can also cause bone spurs. Achilles tendonitis should be diagnosed by your doctor. However, if you experienced a sudden ?pop? in the back of your calf or heel, this might be something more serious like a ruptured or torn Achilles tendon. If this happens, see your doctor immediately.
Causes
Achilles tendinitis is usually caused by straining the Achilles tendon through intense activity or a sudden increase in exercise. Individuals who play basketball often develop Achilles tendinitis as a result of pivoting, jumping, and running. These repetitive movements put pressure on the tendon and can gradually wear it down over time. Increasing the intensity of your workouts may also lead to the development of Achilles tendinitis. This is commonly seen in long distance runners who do quite a bit of uphill running. Similarly, if you start exercising more frequently you may also develop the condition due to overuse of the tendon. Not stretching properly before exercise can also make the tendon more prone to injury. Achilles tendinitis is also common in individuals whose feet have a flattened arch, as this places more stress on the tendon. The condition can also be triggered by arthritis, as joint pain can cause one to compensate by putting more pressure on the Achilles tendon.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary because you can injure various areas of the muscle-tendon complex. The pain may be an acute or chronic sharp, stabbing, piercing, shooting, burning or aching. It is often most noticeable immediately after getting out of bed in the morning, or after periods of inactivity, like sitting down for lunch. After a couple minutes of walking around, it will often then settle down somewhat, before becoming symptomatic again after excessive time standing or walking. But regardless of how the pain is perceived, Achilles tendon pain should not be left untreated due to the danger that the tendon can become weak, frayed, thickened, and eventually it may rupture.
Diagnosis
A doctor examines the patient, checking for pain and swelling along the posterior of the leg. The doctor interviews the patient regarding the onset, history, and description of pain and weakness. The muscles, tissues, bones, and blood vessels may be evaluated with imaging studies, such as X-ray, ultrasound, or MRI.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Use the R.I.C.E method of treatment when you first notice the pain. Although rest is a key part of treating tendonitis, prolonged inactivity can cause stiffness in your joints. Move the injured ankle through its full range of motion and perform gentle calf and ankle stretches to maintain flexibility. If self-care doesn't work, it's important to get the injury treated because if the tendon continues to sustain small tears through movement, it can rupture under excessive stress. Your doctor may suggest a temporary foot insert that elevates your heel and may relieve strain on the tendon. Other possible treatments include special heel pads or cups to wear in your shoes to cushion and support your heel, or a splint to wear at night. Physical therapy may also help allow the tendon to heal and repair itself over a period of weeks.
Surgical Treatment
There are three common procedures that doctor preform in order help heal the tendinitis depending on the location of the tendinitis and amount of damage to the tendon, including: Gastrocnemius recession - With this surgery doctors lengthen the calf muscles because the tight muscles increases stress on the Achilles tendon. The procedure is typically done on people who have difficulty flexing their feet even with constant stretching. Debridement and Repair - When there is less than 50% damage in the tendon, it is possible for doctors to remove the injured parts and repair the healthy portions. This surgery is most done for patients who are suffering from bone spurs or arthritis. To repair the tendon doctors may use metal or plastic anchors to help hold the Achilles tendon in place. Patients have to wear a boot or cast for 2 weeks or more, depending and the damage done to the tendon. Debridement with Tendon Transfer - When there is more the 50% damage done to the Achilles tendon, and Achilles tendon transfer is preformed because the remain healthy tissue is not strong enough. The tendon that helps the big toe move is attached to give added strength to the damaged Achilles. After surgery, most patients don?t notice any difference when they walk or run.
Prevention
There are several things you can do to reduce the risk of Achilles tendinitis, warm up every time before you exercise or play a sport. Switch up your exercises. Slowly increase the length and intensity of your workouts. Keep your muscles active and stay in shape all year-round. When you see symptoms of Achilles tendinitis, stop whatever activity you are doing and rest.
What Brings About Heel Pain And Ways To Deal With It

Overview
Plantar fasciitis is that pain in the bottom of your foot usually felt around your heel. That pain is especially strong with the first few steps in the morning as you are getting out of bed and standing on your feet, or after sitting and resting for awhile. The name Plantar fasciitis comes from: "Plantar" which means something that belongs to the foot, "fascia" which is a band or ligament or a connective tissue, and "itis" which means inflammation. The band connects the heel bone to the bones of the toes. The pain is caused by injuring this tough band on the bottom of the foot.
Causes
The cause of plantar fasciitis is often unclear and may be multifactorial. Because of the high incidence in runners, it is best postulated to be caused by repetitive microtrauma. Possible risk factors include obesity, occupations requiring prolonged standing and weight-bearing, and heel spurs. Other risk factors may be broadly classified as either extrinsic (training errors and equipment) or intrinsic (functional, structural, or degenerative). Training errors are among the major causes of plantar fasciitis. Athletes usually have a history of an increase in distance, intensity, or duration of activity. The addition of speed workouts, plyometrics, and hill workouts are particularly high-risk behaviors for the development of plantar fasciitis. Running indoors on poorly cushioned surfaces is also a risk factor. Appropriate equipment is important. Athletes and others who spend prolonged time on their feet should wear an appropriate shoe type for their foot type and activity. Athletic shoes rapidly lose cushioning properties. Athletes who use shoe-sole repair materials are especially at risk if they do not change shoes often. Athletes who train in lightweight and minimally cushioned shoes (instead of heavier training flats) are also at higher risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
People with this condition sometimes describe the feeling as a hot, sharp sensation in the heel. You usually notice the pain first thing in the morning when you stand. After walking for a period of time, the pain usually lessens or even disappears. However, sharp pain in the center of the heel may return after resting for a period of time and then resuming activity.
Diagnosis
After you describe your symptoms and discuss your concerns, your doctor will examine your foot. Your doctor will look for these signs. A high arch, an area of maximum tenderness on the bottom of your foot, just in front of your heel bone. Pain that gets worse when you flex your foot and the doctor pushes on the plantar fascia. The pain improves when you point your toes down. Limited "up" motion of your ankle. Your doctor may order imaging tests to help make sure your heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis and not another problem. X-rays provide clear images of bones. They are useful in ruling out other causes of heel pain, such as fractures or arthritis. Heel spurs can be seen on an x-ray. Other imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound, are not routinely used to diagnose plantar fasciitis. They are rarely ordered. An MRI scan may be used if the heel pain is not relieved by initial treatment methods.
Non Surgical Treatment
Anti-inflammatory medications can help decrease the inflammation in the arch and heel of your foot. These medications include Advil, Mtrin, Ibuprofen, and Aleve. Use the medication as directed on the package. If you tolerate it well, take it daily for two weeks then discontinue for one week. If symptoms worsen or return, resume for two weeks, then stop. You should eat when taking these medications, as they can be hard on your stomach. Ach Support. Over the counter inserts provide added arch support and soft cushion. Based on the individual needs of your foot, you may require custom inserts. Achilles Tendon Stretch. Pace a shoe insert under your affected foot. Place your affected leg behind your unaffected leg with the toes of your back foot pointed towards the heel of your other foot. Lean into the wall. Bend your front knee while keeping your back leg straight with your heel firmly on the ground. Hold the stretch for a count of 10. A set is 10 repetitions. Perform the stretch at least three times a day.
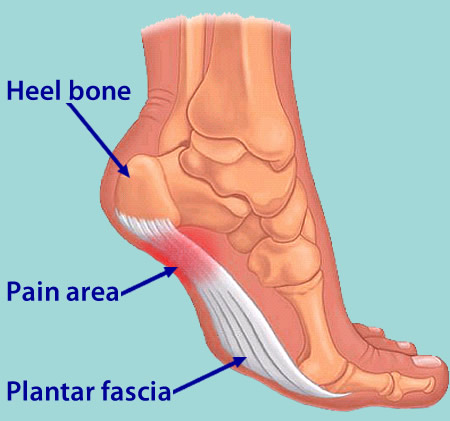
Surgical Treatment
Surgery may be considered in very difficult cases. Surgery is usually only advised if your pain has not eased after 12 months despite other treatments. The operation involves separating your plantar fascia from where it connects to the bone; this is called a plantar fascia release. It may also involve removal of a spur on the calcaneum if one is present. Surgery is not always successful. It can cause complications in some people so it should be considered as a last resort. Complications may include infection, increased pain, injury to nearby nerves, or rupture of the plantar fascia.