What Brings About Heel Pain And Ways To Deal With It

Overview
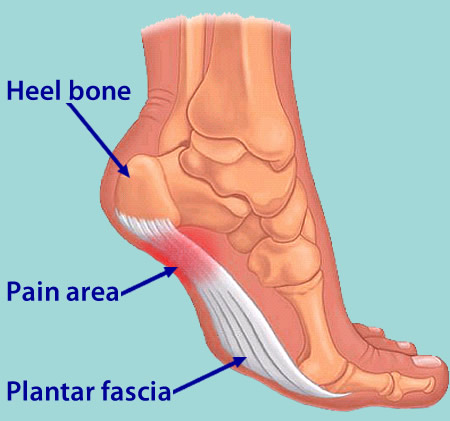
Plantar fasciitis is that pain in the bottom of your foot usually felt around your heel. That pain is especially strong with the first few steps in the morning as you are getting out of bed and standing on your feet, or after sitting and resting for awhile. The name Plantar fasciitis comes from: "Plantar" which means something that belongs to the foot, "fascia" which is a band or ligament or a connective tissue, and "itis" which means inflammation. The band connects the heel bone to the bones of the toes. The pain is caused by injuring this tough band on the bottom of the foot.
Causes
The cause of plantar fasciitis is often unclear and may be multifactorial. Because of the high incidence in runners, it is best postulated to be caused by repetitive microtrauma. Possible risk factors include obesity, occupations requiring prolonged standing and weight-bearing, and heel spurs. Other risk factors may be broadly classified as either extrinsic (training errors and equipment) or intrinsic (functional, structural, or degenerative). Training errors are among the major causes of plantar fasciitis. Athletes usually have a history of an increase in distance, intensity, or duration of activity. The addition of speed workouts, plyometrics, and hill workouts are particularly high-risk behaviors for the development of plantar fasciitis. Running indoors on poorly cushioned surfaces is also a risk factor. Appropriate equipment is important. Athletes and others who spend prolonged time on their feet should wear an appropriate shoe type for their foot type and activity. Athletic shoes rapidly lose cushioning properties. Athletes who use shoe-sole repair materials are especially at risk if they do not change shoes often. Athletes who train in lightweight and minimally cushioned shoes (instead of heavier training flats) are also at higher risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
People with this condition sometimes describe the feeling as a hot, sharp sensation in the heel. You usually notice the pain first thing in the morning when you stand. After walking for a period of time, the pain usually lessens or even disappears. However, sharp pain in the center of the heel may return after resting for a period of time and then resuming activity.
Diagnosis
After you describe your symptoms and discuss your concerns, your doctor will examine your foot. Your doctor will look for these signs. A high arch, an area of maximum tenderness on the bottom of your foot, just in front of your heel bone. Pain that gets worse when you flex your foot and the doctor pushes on the plantar fascia. The pain improves when you point your toes down. Limited "up" motion of your ankle. Your doctor may order imaging tests to help make sure your heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis and not another problem. X-rays provide clear images of bones. They are useful in ruling out other causes of heel pain, such as fractures or arthritis. Heel spurs can be seen on an x-ray. Other imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound, are not routinely used to diagnose plantar fasciitis. They are rarely ordered. An MRI scan may be used if the heel pain is not relieved by initial treatment methods.
Non Surgical Treatment
Anti-inflammatory medications can help decrease the inflammation in the arch and heel of your foot. These medications include Advil, Mtrin, Ibuprofen, and Aleve. Use the medication as directed on the package. If you tolerate it well, take it daily for two weeks then discontinue for one week. If symptoms worsen or return, resume for two weeks, then stop. You should eat when taking these medications, as they can be hard on your stomach. Ach Support. Over the counter inserts provide added arch support and soft cushion. Based on the individual needs of your foot, you may require custom inserts. Achilles Tendon Stretch. Pace a shoe insert under your affected foot. Place your affected leg behind your unaffected leg with the toes of your back foot pointed towards the heel of your other foot. Lean into the wall. Bend your front knee while keeping your back leg straight with your heel firmly on the ground. Hold the stretch for a count of 10. A set is 10 repetitions. Perform the stretch at least three times a day.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery may be considered in very difficult cases. Surgery is usually only advised if your pain has not eased after 12 months despite other treatments. The operation involves separating your plantar fascia from where it connects to the bone; this is called a plantar fascia release. It may also involve removal of a spur on the calcaneum if one is present. Surgery is not always successful. It can cause complications in some people so it should be considered as a last resort. Complications may include infection, increased pain, injury to nearby nerves, or rupture of the plantar fascia.